1. Introduction¶
This user guide describes how to deploy Acumos platforms using the “One Click deploy” tools designed for those who want a simple and automated way to deploy an Acumos platform.
1.1. What is an AIO deploy?¶
By default, the AIO deploy tools build an all-in-one instance of Acumos, with all Acumos data and components running under docker or kubernetes (k8s) on a single virtual machine or physical host machine.
For k8s based deployments, both generic (standard k8s project tools) and OpenShift (RedHat’s k8s distribution) are supported.
Options allow the user to deploy the platform:
- on a cluster of k8s nodes (note: distributing specific components across nodes based upon node labels is planned for future releases)
- with a subset of the components
- to use some components that have previously deployed somewhere, e.g. as a shared service
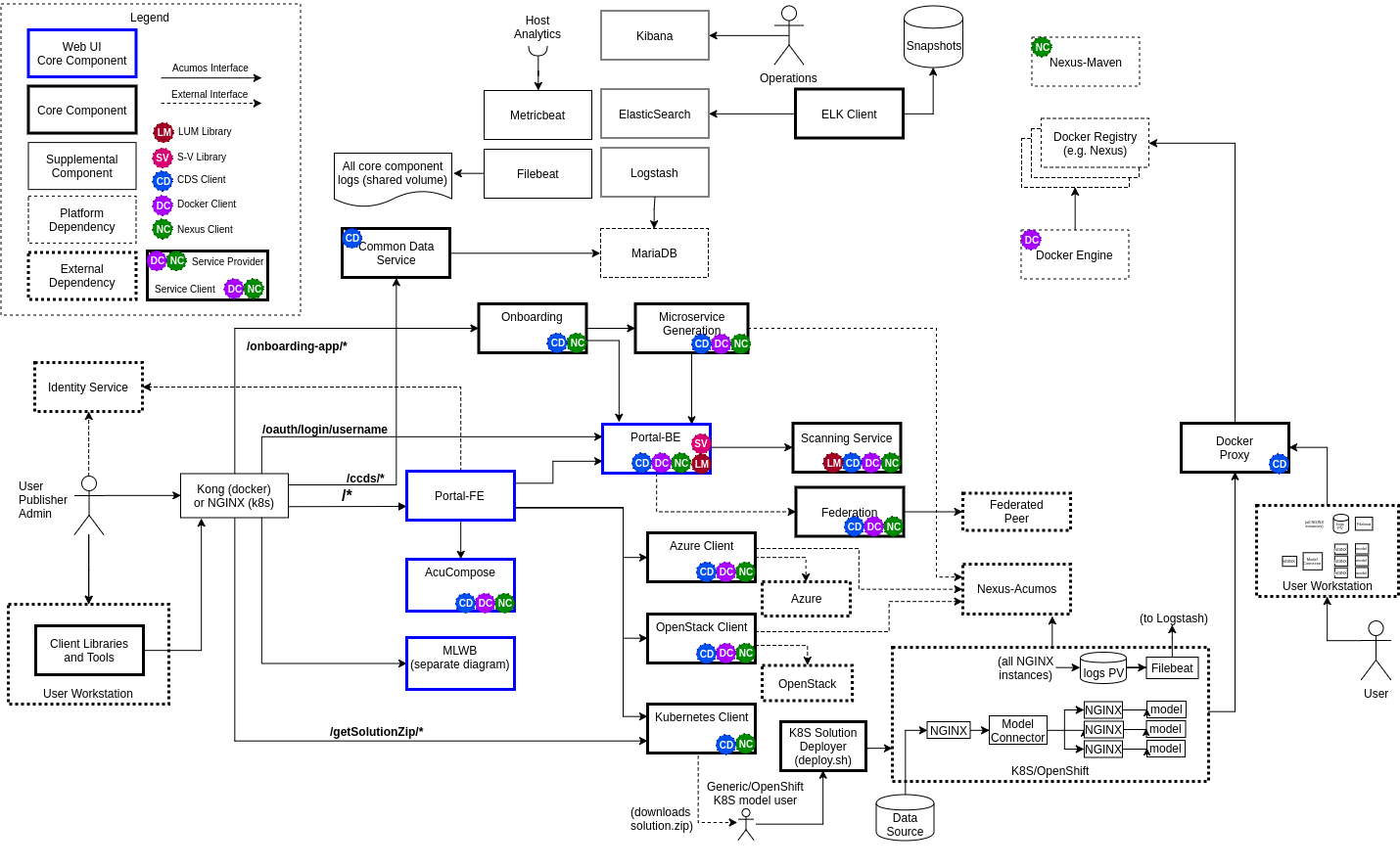
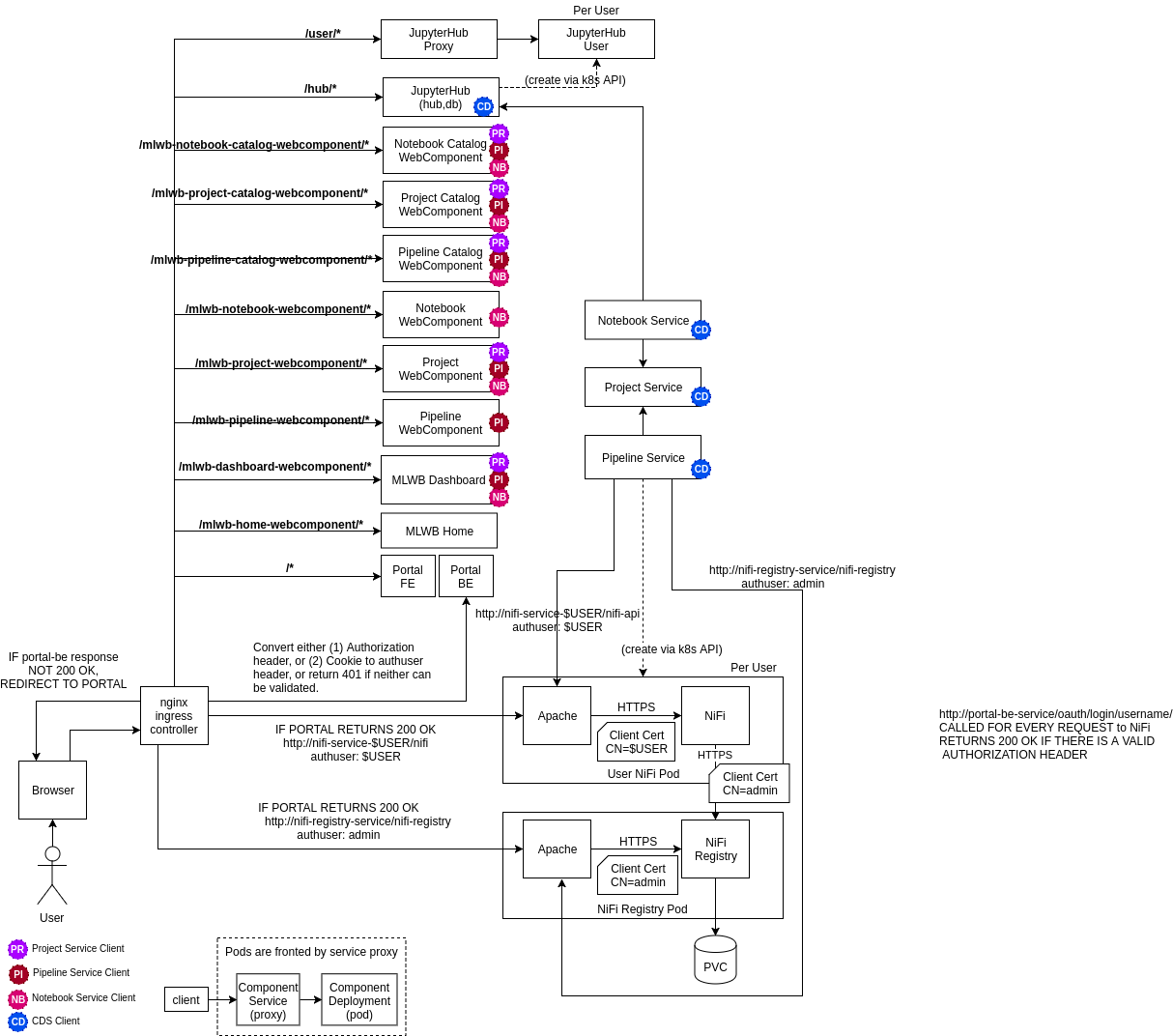
The resulting Acumos platform is illustrated in the following two figures, the first representing the overall architecture, and the second the architecture of the MLWB (Machine-Learning Workbench) subsystem.
2. Quickstart Guide to Platform Deployment (TL;DR)¶
NOTICE:
- this process will remove/install software on your host, and configure it e.g. firewall and security rules. Only execute this process if you understand the implications or are executing the process in a VM/host that you can easily re-create.
- by default, the Acumos platform is deployed with service exposure options typical for development environments. Production environments and especially public environments will need additional planning and restrictions on exposed services, that otherwise could expose your host to security risks. See Security Considerations for recommendations on what/how to lock down as needed, for exposure of an AIO-based Acumos platform outside development/test environments.
Please make sure you review the host prerequisite requirements under Host/VM Preparation.
See these specific sections based upon how you want to deploy the platform:
- if you have a server/VM or existing k8s cluster upon which you want to install the Acumos platform under k8s, using your local workstation to manage the platform, see Deploying from Your Workstation, via the AIO Deployer Tool
- if you have a server/VM upon which you want to directly install/manage the
Acumos platform under k8s, see:
- Deploying as a Privileged (sudo) User if you are a sudo user on that server/VM, and want to deploy/manage the platform under your own account
- Preparation by Host Admin with Platform Deployment by Normal (non-sudo) User if you are a sudo user on the server/VM, and want to prepare the server/VM for another to install/manage the platform upon.
- Docker Based Deployment, if you want to use the legacy docker-compose based method of installation. NOTE not all Boreas release features are supported under docker-compose.
2.1. Kubernetes Based Deployment¶
The process below will support deployment under either a generic kubernetes distribution, or the OpenShift kubernetes distribution. The scripts will detect which distribution is installed and deploy per the requirements of that distribution.
2.1.1. Deploying from Your Workstation, via the AIO Deployer Tool¶
This process supports users with the role of either a cluster admin (full rights to manage cluster resources) or namespace admin (rights to manage resources under a namespace). It also minimizes any dependencies/customization of the user’s workstation, by use of a docker container built specifically for deploying and managing the Acumos platform.
A typical use case for this method is a user who will manage the Acumos platform on the k8s cluster using kubectl executed from their workstation, after basic prerequisites have been arranged by the cluster admin:
- allocation of a namespace
- allocation of a platform FQDN (with DNS registration), external IP, and setup of an ingress controller for the namespace/FQDN
- setup of persistent volume (PV) resources per Acumos requirements (default
recommended allocations are shown below)
- logs: 1Gi
- if deployed as part of the platform, vs use of external instances of these services
- MariaDB: 10Gi
- Nexus (Maven repos and docker registry): 10Gi
- docker-in-docker cache: 5Gi
- NiFi Registry: 5Gi
- NiFi users: 5Gi (for each user)
- JupyterHub: 1Gi
- Jupyter users: 10Gi (for each user)
- Elasticsearch: 10Gi
As an option, a user that has cluster admin role can include these prerequisite steps in the process below.
To use this process, the script aio_k8s_deployer.sh in the tools/aio_k8s_deployer folder is used, with these prerequisite steps:
the user has installed, or has access to, a remote k8s cluster (single/multi-node)
if the k8s cluster does not provide an ingress service with a registered DNS name for the platform ingress, the user needs to ensure that the external IP address to be used by the ingress controller is registered in DNS or configured in the hosts file of their workstation.
the user has installed a bash shell and docker on their workstation
the user has copied the aio_k8s_deployer folder contents (e.g. from a system-integration repo clone) to their workstation, and cloned/copied the system-integration repo into the “deploy” subfolder. For example:
$ mkdir ~/acumos $ git clone "https://gerrit.acumos.org/r/system-integration" $ cp -r system-integration/tools/aio_k8s_deployer/* ~/acumos/. $ cp -r system-integration ~/acumos/deploy/.- the deploy subfolder will be later mapped into the root folder of the acumos-deploy docker container image by the aio_k8s_deployer.sh script.
- the aio_k8s_deployer.sh script and the files in the deploy subfolder have been
customized as desired, including these files in the “deploy” subfolder
- k8s configuration file “kube-config”; this will be used in the container, to access the cluster via kubectl
- (optional) an environment customization script “customize_env.sh”, based upon the sample script customize_env.sh, to override the default environment variables for Acumos, MLWB, MariaDB, and ELK
- (optional) updated the Dockerfile, as desired
- (optional) a post-deploy script, which can include any actions the user wants to automatically occur after the platform is installed, e.g. creation of user accounts, model onboarding; by default the aio_k8s_deployer.sh script will invoke a script named ‘post_deploy.sh’ if present in the deploy subfolder.
To prepare the k8s environment and install using the aio_k8s_deployer:
- using bash, the user runs the following command to create the “acumos-deploy” docker image
$ bash aio_k8s_deployer.sh build
- if the user has a cluster admin role, the user runs the following command
to setup typical prerequisites on the k8s master, e.g.
- apply the environment customizations in customize_env.sh
- cleans the ~/system-integration folder on the sudo user’s account
- copies just the needed system-integration folders to that account
- executes the setup_prereqs.sh script, and saves a log on the local host
- copies the updated system-integration folders/env back to the local host
$ bash aio_k8s_deployer.sh prep <host> <user>
- where:
- <host>: hostname of the k8s master node to execute the steps on
- <user>: sudo user on the k8s master node
- the user then runs the following command to deploy the platform, which
- starts the acumos-deployer container
- updates the AIO tools environment to run under the container
- executes oneclick_deploy.sh, and saves a log
- executes the post_deploy.sh script, if present
- copies the updated files from the acumos-deployer container to the user’s workstation deploy subfolder, incuding the log files and all updated files under the system-integration repo
$ bash aio_k8s_deployer.sh deploy <host> [add-host]
- where:
- <host>: name to suffix to the docker container, to identify the customized container for use with a specific deployment instance
- [add-host]: (optional) value to pass to docker as add-host option
- See When Deployment is Complete for further steps
2.1.2. Deploying as a Privileged (sudo) User¶
This process is for a user that wants to execute all steps in the deployment process using their host account. To deploy the Acumos platform with the default options, as a user on a linux host with at least 16GB RAM and admin (sudo) permission, follow the process below.
clone the system-integration repo
$ git clone https://gerrit.acumos.org/r/system-integration
using bash, check if the user is part of the docker group, and add if not
$ if [[ "$(id -nG "$USER" | grep docker)" == "" ]]; then sudo usermod -aG docker $USER; fi
- if you see “usermod: group ‘docker’ does not exist”, install docker (e.g. using setup_docker.sh in the system-integration/tools folder) and run the command above again. Once you do not see the message above, logout and re-login.
if you don’t have an existing k8s cluster, run the following command to setup a cluster.
$ bash system-integration/tools/setup_k8s_stack.sh setup
execute the following command to install/configure prerequisites, including k8s, MariaDB, and the ELK stack, using your user account, and the hostname or domain name you will use to access the deployed platform.
$ bash system-integration/AIO/setup_prereqs.sh k8s <domain> $USER <generic|openshift> 2>&1 | tee aio_prep.log
When you see “Prerequisites setup is complete.” as the result of the command above, execute the following commands to complete platform setup
$ cd system-integration/AIO $ bash oneclick_deploy.sh 2>&1 | tee aio_deploy.log
The commands above include saving of the detailed deployment actions to a log file ‘deploy.txt’. This can be helpful in getting support from the Acumos project team, to overcome issues you might encounter. If you don’t want to save the log, just leave out the part of the commands above that starts with the ‘pipe’ (‘|’).
As described above, if you don’t need to save the deploy logs, leave out the the part of the commands above that starts with the ‘pipe’ (‘|’).
See When Deployment is Complete for further steps
2.1.3. Preparation by Host Admin with Platform Deployment by Normal (non-sudo) User¶
This process is for a host Admin (sudo user) to prepare the host for a normal (non-sudo) user that will complete the platform deployment, under their account on the host.
Admin completes steps in the previous section, through setup of a k8s cluster
Admin executes the following command to install/configure prerequisites, including k8s, MariaDB, and the ELK stack, using their account. <user> in this case is the username of the normal user that will complete the deployment.
$ bash system-integration/AIO/setup_prereqs.sh k8s <domain> $USER <generic|openshift> 2>&1 | tee aio_prep.log
- When prerequisites setup is complete, the resulting environment files and system-integration clone will have been copied to the user account.
The user executes the following commands to complete platform setup
$ cd system-integration/AIO $ bash oneclick_deploy.sh 2>&1 | tee aio_deploy.log
As described above, if you don’t need to save the deploy logs, leave out the the part of the commands above that starts with the ‘pipe’ (‘|’).
See When Deployment is Complete for further steps
2.2. Docker Based Deployment¶
NOTE: Not all Acumos features will work as expected under docker, so those will not be deployed. Examples include the new services in support of model training.
To deploy the components that do work under docker, follow the instructions in the sections below.
2.2.1. Prerequisites for Docker Based Deployment¶
Prerequisites for docker based deployment:
- Deployment is supported only on Ubuntu Xenial (16.04), Bionic (18.04), or Centos 7 hosts
- All hostnames or FQDNs specified in environment files must be DNS-resolvable (entries in /etc/hosts or in an actual DNS server)
- User running this script
- has sudo privileges
- has installed docker per system-integration/tools/setup_docker.sh
- has added themselves to the docker group (sudo usermod -aG docker $USER), and re-logged-in to activate docker group membership
- if deploying in preparation for use by a non-sudo user, has created the user account (sudo useradd -m <user>)
- has cloned or otherwise provided the system-integration repo, in the user’s home folder
- has customized or created as needed
- the main environment file system-integration/AIO/acumos-env
- ELK-stack environment: see
system-integration/charts/elk-stack/setup_elk_env.sh as a guide to what
environment values can be customized. Customize the default values in
that script, by changing the values after ‘:-” e.g. to change “true” to
“false” replace the first line below with the second
- export ACUMOS_DEPLOY_METRICBEAT=”${ACUMOS_DEPLOY_METRICBEAT:-true}”
- export ACUMOS_DEPLOY_METRICBEAT=”${ACUMOS_DEPLOY_METRICBEAT:-false}”
- MariaDB: as for the ELK_stack, customize system-integration/charts/mariadb/setup_mariadb_env.sh
2.2.2. Deploying for Yourself, as a Host Admin (sudo user)¶
NOTE: If you are deploying into an Azure-based VM, pay attention to this special configuration need for the docker-engine; update the acumos_env.sh (in system-integration/AIO) script to set the ACUMOS_DEPLOY_DOCKER_DIND flag to “false”, which will ensure that the docker-dind service is not installed. Docker-dind has known issues under Azure.
export ACUMOS_DEPLOY_DOCKER_DIND=false
If deploying the platform for yourself, run these commands:
cd system-integration/AIO/ bash setup_prereqs.sh docker <domain> $USER 2>&1 | tee aio_deploy.log bash oneclick_deploy.sh 2>&1 | tee -a aio_deploy.log
- where:
- <domain> is the name you want to use for the Acumos portal. This can be a hostname or FQDN.
- See When Deployment is Complete for further steps
2.2.3. Preparing as a Host Admin, with Platform Deployment as a Normal User¶
If a Host Admin needs to run the privileged-user steps for a normal user that will take it from there:
NOTE: If you are deploying into an Azure-based VM, pay attention to this special configuration need for the docker-engine; update the acumos_env.sh (in system-integration/AIO) script to set the ACUMOS_DEPLOY_DOCKER_DIND flag to “false”, which will ensure that the docker-dind service is not installed. Docker-dind has known issues under Azure.
export ACUMOS_DEPLOY_DOCKER_DIND=false
As the Host Admin, run these commands:
cd system-integration/AIO/ bash setup_prereqs.sh docker <domain> <user> 2>&1 | tee aio_deploy.log
- where:
- <domain> is the name you want to use for the Acumos portal. This can be a hostname or FQDN.
- <user> use the normal user’s account name on the host
- where:
As the normal user, run this command
bash oneclick_deploy.sh 2>&1 | tee -a aio_deploy.log
As described above, if you don’t need to save the deploy logs, leave out the the part of the commands above that starts with the ‘pipe’ (‘|’).
2.2.4. When Deployment is Complete¶
When deployment has completed, you should see a success message with a set of URLs to access the various platform services. You can also view the file “acumos.url” which will be in the system-integration/AIO folder (example below)
You can access the Acumos portal and other services at the URLs below,
assuming hostname "acumos.example.com" is resolvable from your workstation:
Portal: https://acumos.example.com
Common Data Service Swagger UI: https://acumos.example.com/ccds/swagger-ui.html
- if you have issues with using the CDS swagger over HTTPS, try the HTTP link
http://$ACUMOS_DOMAIN:$ACUMOS_CDS_NODEPORT/ccds/swagger-ui.htm
Portal Swagger UI: https://acumos.example.com/api/swagger-ui.html
Onboarding Service Swagger UI: https://acumos.example.com/onboarding-app/swagger-ui.html
Kibana: http://acumos.example.com:30561/app/kibana
Nexus: http://acumos.example.com:30881
By default, the platform is not configured to require email confirmation of new accounts, so you can create a new account directly on the Portal home. To create an account with the Admin role (needed for various platform admin functions), use the create_user.sh script in the system-integration/tests folder
3. Release Scope¶
3.1. Current Release (Boreas)¶
The Acumos wiki describes the principle goals and related deployment scenarios supported by the AIO toolset, and regularly verified in testing.
3.1.1. What’s included in the AIO tools¶
In system-integration repo folder AIO:
- setup_prereqs.sh: Script to be used by a host admin (a user with privilege to install applications and configure the host) to prepare a host for a normal user to later deploy/manage the Acumos platform there. Typically used for lab environments.
- oneclick_deploy.sh: the main script that kicks off the deployment, to setup an AIO instance of Acumos under a docker or kubernetes environment.
- acumos_env.sh: environment setup script that is customized as new environment parameters get generated (e.g. passwords). Used by various scripts in this toolset, to set shell environment variables that they need.
- setup_acumosdb.sh: script that initializes the Acumos database under MariaDB.
- setup_keystore.sh: script that enables use of pre-configured CA and server certificates for an Acumos platform, or creation of new self-signed certificates.
- docker_compose.sh: Script called by the other scripts as needed, to take actions on the set of Acumos docker services. Used by oneclick_deploy.sh and clean.sh for docker-based deployments. You can also call this directly e.g. to tail the service container logs. See the script for details.
- utils.sh: utility script containing functions used by many of these scripts.
- redeploy_component.sh: Script that allows the redeployment of a single component.
- clean.sh: if needed, this script allows a privileged user to remove all components and dependencies of the Acumos platform installed by the tools above.
In AIO/beats:
- deployment scripts and templates for the Filebeat and Metricbeat services as ELK stack components deployed along with the Acumos platform.
In AIO/certs:
- setup_certs.sh: creates self-signed certificates (CA and server), keystore, and truststore for use by core platform components.
In AIO/docker/acumos:
- docker-compose yaml files and deployment script for Acumos core components.
In AIO/certs:
- setup_certs.sh: script to create self-signed CA and server certs.
- This folder is also used to stage user-provided certs to be used in Acumos platform deployment.
In AIO/docker-engine:
- scripts and templates to deploy docker-in-docker as the docker-engine service for k8s-based Acumos platforms, or the docker-engine service on the AIO host
In AIO/docker-proxy:
- scripts and templates for deployment of the docker-proxy core component of the Acumos platform
In AIO/elk-stack:
- scripts and templates to deploy the ELK stack core components under docker
In AIO/ingress:
- scripts and templates to deploy the NGINX Ingress Controller for Kubernetes, and ingress rules for Acumos core components.
In AIO/kong:
- scripts and templates to deploy the Kong service as an ingress controller for the Acumos platform, as deployed under docker
In AIO/kubernetes:
- under deployment, kubernetes deployment templates for all system components
- under service, kubernetes service templates for all system components
- under configmap, kubernetes configmap templates for all system components
- under rbac, kubernetes role-based access control templates enabling system components to invoke kubernetes cluster operations
In AIO/mariadb:
- scripts and templates to deploy the MariaDB under docker, as the Acumos platform database backend service
In AIO/nexus:
- scripts and templates to deploy the Nexus service for the Acumos platform
In charts:
- scripts and templates to deploy the following components for k8s-based
deployments, using Helm as deployment tool
- elk-stack: ELK stack core components
- jupyterhub: the JupterHub/JupyterLab services for notebook-based model development
- mariadb: MariaDB service
- nifi: the NiFi service for data pipeline development
- zeppelin: the Zeppelin service for notebook-based model development
- NOTE: Zeppelin deployment is a single, multi-user instance which is provided for experimental use in Boreas. Single-user instance deployment is coming in the next release (Clio).
In tests:
- peer_test.sh: Peering and marketplace subsciptions setup for two AIO platforms. Used to test federation use cases.
- create_peer.sh: Automated setup of a peer relationship between two Acumos AIO deployments. Used by peer_test.sh.
- create_user.sh: Automated user provisioning and role assignment. Used by scripts in this repo to create default admin accounts. Can also be used to create user accounts for testing or platform use.
- create_subscription.sh: creates a federation subscription for all models published by a federated Acumos platform.
- bootstrap_models.sh: Model package onboarding via curl, for all models in a folder.
- onboard_model.sh: Model package onboarding via curl.
- license_scan.sh: invokes a license scan for a solution, using the Security Verification Scanning Service.
In tools:
- aio_k8s_deployer: deployment script and configuration to deploy Acumos under k8s using a docker container based approach, which minimizes dependencies on the user workstation
- add_host_alias.sh: adds a host alias to an Acumos core component, e.g. for hostnames/FQDNs that are not resolvable through DNS.
- setup_docker.sh: deploys the docker version used for docker-based platform deployment and interaction.
- setup_helm.sh: deploys Helm as a service deployment tool.
- setup_k8s.sh: deploys a generic k8s cluster.
- setup_kubectl.sh: deploys and uses the kubectl tool used by other scripts and the user to manage and interact with generic k8s based deployments.
- setup_mariadb_client.sh: deploys the MariaDB client as used by other scripts to configure the Acumos database.
- setup_openshift.sh: deploys an OpenShift Origin 3.11 kubernetes cluster, for subsequent Acumos platform deploymet on Centos 7 servers.
- setup_openshift_client.sh: deploys the OpenShift client (oc) tool used by other scripts and users to manage and interact with OpenShift based platform deployments.
- setup_prometheus.sh: deploys the Prometheus monitoring service, with Grafana as a data visualization tool, for monitoring the Acumos platform’s resources at the k8s level. Also deploys Grafana dashboards in the dashboards folder.
- setup_pv.sh: deploys host-based persistent volumes for use with docker and k8s-based platform deployments.
4. Deployment Step-by-Step Guide¶
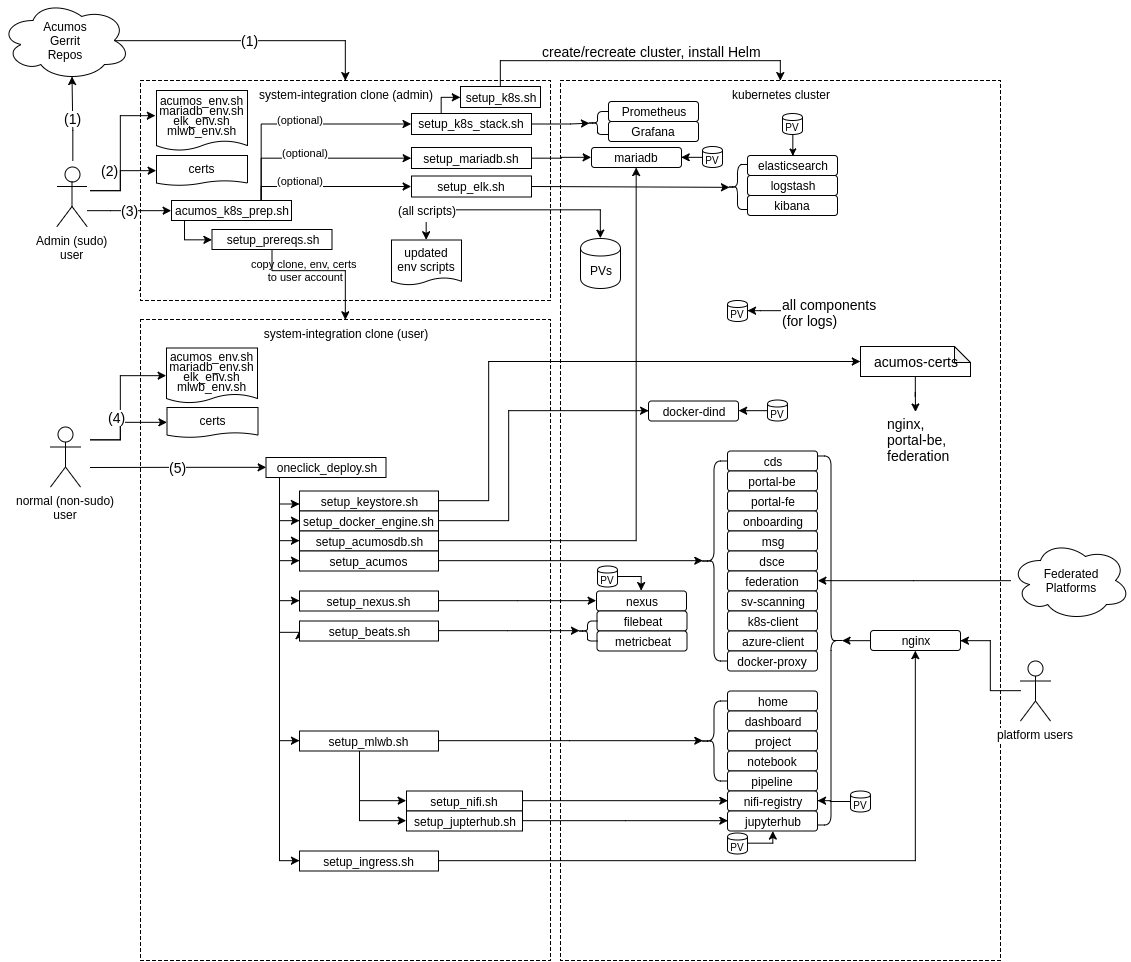
The steps in this process are illustrated by the following figure. Note this figure refers to kubernetes, but the same basic process applies for docker.
Prerequisites for each step are described for the step, under Pre-Arrangement of Ingress Certs, Install Host Preparation by Admin, and Platform Deployment.
- Host Admin clones the system-integration repo, or uses a local/customized clone.
- Host Admin customizes the environment files and/or certs as desired, per Pre-Arrangement of Ingress Certs
- The Admin runs the applicable host preparation script(s) as described in Install Host Preparation by Admin
- The user (Admin, if installing for their self) further updates the environment files and certs as desired, per Platform Deployment
- The user deploys the rest of the platform components via script ‘oneclick_deploy.sh’, per Platform Deployment
4.1. Host/VM Preparation¶
For developer-focused AIO deployments, it’s assumed that the developer has a minimum of one host machine (physical workstation/server or VM) that they will use for the platform.
The AIO platform is also deployable on a cluster of machines or in a multi-node kubernetes cluster, but note:
- for docker-based deployment, the AIO toolset supports limited distribution of components across nodes, primarily the backend services (Nexus, MariaDB, ELK, …), in addition to the core platform components in one node
- for kubernetes-based deployment, the components will be distributed across nodes in a kubernetes cluster per the default scheduling configuration of the cluster
Following are basic requirements for single-node/AIO machines:
- minimum 16 GB RAM (32 GB or more recommended)
- minimum 2 core/vCore (4 or more recommended)
- minimum 1 network interface
- network security rules in place to allow incoming traffic on the following ports:
4.2. Pre-Arrangement of Ingress Certs¶
If you deploy the AIO platform often or in multiple test environments, you may find it useful to pre-arrange the ingress certs that will be used to access the platform(s), either using commercial cert providers, or the self-signed cert tools provided in the system-integration repo. This allows you and users for example to use web browser tools to trust self-signed certs, avoiding browser warnings.
The Acumos tool supporting creation of self-signed certs is in system-integration/AIO/certs/setup_certs.sh. An example is given below, showing how to select the parameters for setting up a cert and related files that are usable on multiple hosts, by hostname/domain and IP address:
- This script is invoked as:
bash setup_certs.sh <name> <subject-name> ["alt-names"] ["alt-ips"]
Where:
- name: name prefix to use in the generated files (e.g. acumos)
- subject-name: primary domain name to associate
- alt-names: quoted, space-delimited set of alternate names
- alt-ips: quoted, space-delimited set of alternate IP addresses
as in the example:
cd system-integration/AIO/certs
bash setup-certs.sh acumos acumos \
"test01 test02 test03 acumos-test04.eastus.cloudapp.azure.com" \
"10.1.0.2 10.1.0.3 10.1.0.4 10.1.0.5"
This will generate the following files:
- acumos-ca.key: self-signed CA private key
- acumos-ca.crt: self-signed CA certificate
- acumos.key: server cert private key
- acumos.crt: server cert
- acumos-keystore.p12: PKCS12 format keystore with server cert
- acumos-truststore.jks: JKS format truststore with CA cert
- cert_env.sh: environment file with the related passwords
NOTE: the process below has not been verified. If you need to following this process and encounter issues, reach out to the Acumos Community mail list for help.
To use commercial certs with the Acumos AIO platform, follow these steps:
place the server cert and private key in folder system-integration/AIO/certs
update related values in system-integration/AIO/acumos_env.sh and put these commands into a file system-integration/AIO/cert_env.sh
- export ACUMOS_CERT_PREFIX=<prefix you want to use for your keystore/truststore
- export ACUMOS_CERT=<name of the server cert file)
- export ACUMOS_CERT_KEY=<name of the server cert private key file>
- export ACUMOS_CERT_KEY_PASSWORD=<passphrase for the cert private key>
run the commands below, which create the keystore and truststore for Acumos
cd system-integration/AIO/certs source cert_env.sh KEYSTORE_PASSWORD=$(uuidgen) echo "export KEYSTORE_PASSWORD=$KEYSTORE_PASSWORD" >>cert_env.sh openssl pkcs12 -export \ -in $ACUMOS_CERT \ -inkey $ACUMOS_CERT_KEY \ -passin pass:$CERT_KEY_PASSWORD \ -certfile $ACUMOS_CERT \ -out $ACUMOS_CERT_PREFIX-keystore.p12 \ -passout pass:$KEYSTORE_PASSWORD TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD=$(uuidgen) echo "export TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD=$TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD" >>cert_env.sh keytool -import \ -file $ACUMOS_CERT \ -alias $ACUMOS_CERT_PREFIX-ca \ -keystore $ACUMOS_CERT_PREFIX-truststore.jks \ -storepass $TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD -noprompt
4.3. Install Host Preparation by Admin¶
NOTE: If you are deploying under k8s into an Azure-based VM, pay attention to the special configuration need for the docker-engine, as described below.
Prerequisites:
Ubuntu Xenial/Bionic or Centos 7 server
All hostnames specified in acumos_env.sh must be DNS-resolvable on all hosts (entries in /etc/hosts or in an actual DNS server)
For deployments behind proxies, set ACUMOS_HTTP_PROXY and ACUMOS_HTTPS_PROXY in acumos_env.sh
Admin user running this script has:
- Installed docker per system-integration/tools/setup_docker.sh
- Added themselves to the docker group (sudo usermod -aG docker $USER)
- Logged out and back in, to activate docker group membership
Initial basic setup (manual)
If you are an Admin and deploying the platform for a normal user, assuming the non-sudo user is “acumos”
sudo useradd -m acumos
This process prepares the host with prerequisites that normal users do not have permission to arrange. This includes:
- installing software packages
- configuring host settings
- creating folders for host-mapped volumes
The Admin user will follow this process:
‘install root folder’ refers to the Admin user’s home folder. Installation in other root folders is a work in progress, and not yet fully verified.
create in the install root folder a subfolder “acumos” and folders “env”, “logs”, “certs” under it.
in the install root folder, clone the system-integration repo (branch, tag, commit, or master), and make any desired updates to it (e.g. checkout a specific patch)
If you are deploying the platform under k8s in an Azure VM, update acumos_env.sh (in system-integration/AIO) script to set the ACUMOS_DEPLOY_DOCKER_DIND flag to “false”, which will ensure that the docker-dind service is not installed. Docker-dind has known issues under Azure.
export ACUMOS_DEPLOY_DOCKER_DIND=false
If you are deploying under docker, run the command
bash setup_prereqs.sh <under> <domain> <user>
- under: docker (install prereqs for docker or k8s based deployment)
- domain: FQDN of platform
- user: user that will be completing Acumos platform setup via
- oneclick_deploy.sh (if installing for yourself, use $USER)
If you are deploying under k8s, and do not have an existing k8s cluster or need to deploy a new cluster e.g. an AIO cluster on a VM, run the command below on the host for the new cluster
bash system-integration/tools/setup_k8s_stack.sh setup
If you are deploying under k8s, run the command
bash system-integration/AIO/setup_prereqs.sh k8s <domain> $USER <generic|openshift>
- k8s: indicates deployment under k8s
- user: non-sudo user account (use $USER if deploying for yourself)
- domain: domain name of Acumos platorm (resolves to this host)
- generic|openshift: use generic k8s or openshift
When the process is complete, the updated system-integration clone and environment will have been copied to the platform deployment user’s home folder. If you are deploying the platform for yourself, proceed to the next section. If preparing the platform for a normal user, the user should execute the process in the next section.
4.4. Platform Deployment¶
The script supporting this step is system-integration/AIO/oneclick_deploy.sh.
Prerequisites:
- User workstation is Ubuntu Xenial/Bionic, Centos 7, or MacOS
- setup_prereqs.sh run by a sudo user
- As setup by those scripts, a user home folder “acumos” with subfolders “env”, “logs”, and “certs”. These folders are created by the prerequisites scripts principally as a backup to the environment files under system-integration/AIO.
This process deploys the Acumos platform with the options selectable by the user, e.g.
- any option selectable through the environment files, which can be customized
in the backup folder “acumos/env” or directly in the system-integration clone
under:
- ~/system-integration/AIO/acumos/env/acumos_env.sh
- ~/system-integration/AIO/acumos/env/mariadb_env.sh
- ~/system-integration/AIO/acumos/env/elk_env.sh
- ~/system-integration/AIO/mlwb/mlwb_env.sh
- NOTE
- a detailed description of the customizable environment values is not provided here, but the Acumos community can assist you with any support questions you may have via the Acumos Community mail list
- use of pre-created certs per Pre-Arrangement of Ingress Certs
- if you updated the environment files or certificates under ~/acumos, prior
to running the deployment command below, copy those updates into the
system-integration clone:
- cp ~/acumos/env/* ~/system-integration/AIO/.
- cp ~/acumos/certs/* ~/system-integration/AIO/certs/.
To deploy the rest of the platform components, run the commands:
cd ~/system-integration/AIO bash oneclick_deploy.sh
When the process is complete, you will see a set of URLs to the main platform component/UI features, as described above.
4.5. Updating Configuration and Components¶
Changes to the configuration can be applied as described in the previous section. Note that if you are making changes to the configuration of a deployed platform, some changes may break some aspects of the platform, so be careful.
The most commonly updated configuration items include:
- in acumos_env.sh
- component versions
- component hosts and ports, e.g. for reuse of previously deployed components, e.g. a shared docker-engine, docker registry, MariaDB, Nexus, or ELK stack service
- component credentials (user and/or password)
- ports, to avoid conflict with other deployments in the same environment
- Nexus repo details
- HTTP proxy
- CDS (Common Dataservice) database version
- model onboarding tokenmode
- operator ID
- kubernetes namespace
- Persistent Volume options
- docker-compose templates in AIO/docker/acumos or kubernetes templates in
AIO/kubernetes
- Note: make sure the template modifications are compatible with previously deployed components, and the version of the related Acumos component you are deploying/re-deploying
4.6. Stopping, Restarting, Redeploying¶
Note: the following sections assume that you have deployed the Acumos platform from the system-integration folder in your user home directory, i.e. “~/”.
If you just want to redeploy Acumos components, without affecting any data in the MariaDB or Nexus, be sure to set these variables in AIO/acumos_env.sh:
export ACUMOS_DEPLOY_MARIADB=false
export ACUMOS_SETUP_DB=false
export ACUMOS_DEPLOY_NEXUS=false
To stop components running under docker and remove the containers, execute the following commands from the “docker” folder related to the type of component, referencing the related docker-compose yaml file as “<yml>”:
cd ~/system-integration/<docker folder>
source ~/system-integration/AIO/acumos_env.sh
docker-compose -f acumos/<yml> down
The related docker folders are:
- AIO/docker, for Acumos core components azure-client, common-data-svc, dsce (AcuCompose), federation, kubernetes-client, microservice-generation, onboarding, portal-be, portal-fe, sv-scanning
- AIO/docker-proxy/docker, for the docker-proxy core component
- AIO/mlwb/docker, for the MLWB components
- AIO/nexus/docker, for nexus
- AIO/mariadb/docker, for mariadb
- AIO/kong/docker, for kong
- AIO/elk-stack/docker, for the core ELK-stack components elasticsearch, logstash, kibana
- AIO/beats/docker, for the “beats” components filebeat, metricbeat
To restart these components, e.g. after updating the related configuration files, issue the following command:
cd ~/system-integration/<docker folder>
source ~/system-integration/AIO/acumos_env.sh
docker-compose -f acumos/<yml> up -d --build
If you want to automatically stop and redeploy the components in one command:
for Acumos core components (azure-client-service, cds-service, dsce-service, federation-service, kubernetes-client-service, msg-service, onboarding-service, portal-be-service, portal-fe-service, sv-scanning-service)
bash ~/system-integration/AIO/redeploy_component.sh <component>
for the other components, a specific redeployment script is provided in the related folder (docker-proxy, mlwb, nexus, mariadb, kong, elk-stack, beats)
bash ~/system-integration/AIO/<folder>/setup_*.sh ~/system-integration/AIO/
Because kubernetes-based components may depend upon a variety of other kubernetes resources specific to them or shared with other components (e.g. configmaps, secrets, PVCs), simply redeploying the specific components after any required configuration updates is recommended.
The configuration files specific the components are generally under a subfolder “kubernetes”, and are specific to the type of resource (e.g. service, deployment, configmap, secret, PVC, etc). Once you have updated these as needed, you can’ redeploy the component and any resources specific to it (not shared) via the command:
for core components under AIO/kubernetes/deployment, using the component names per the “app:” value in the related deployment template (azure-client, cds, dsce, federation, kubernetes-client, msg, onboarding, portal-be, portal-fe, sv-scanning):
bash ~/system-integration/AIO/redeploy_component.sh <component>
for the other components, running the related “setup_*.sh” command as described for docker
If you just need to stop a component, use the following command and reference the related “app” label:
kubectl delete deployment -n acumos -l app=<app>
You can see all the component-related “app” labels via the command:
kubectl get deployment -n acumos -o wide
After stopping the component, you can redeploy it as needed using the methods described above.
5. Logs Location¶
Logs are easily accessible on the AIO host under /mnt/<ACUMOS_NAMESPACE>/logs directory (‘<ACUMOS_NAMESPACE>’ is by default ‘acumos’). That directory is mounted by most Acumos components as their log directory.
6. Security Considerations¶
As noted in Introduction, the AIO deployment approach includes various development/test environment-enabling aspects, that for a more “production” or publicly-exposed deployment, should be reconsidered and as needed, locked down.
For k8s-based platforms, some of these aspects are related to work-in-progress on more fully supporting platform exposure through ingress controllers. An ingress controller is a convenient place to apply subnet-based restrictions on service access. See the NGINX ingress annotations guide for whitelist-source-range for more information. Following are the services exposed in the Acumos platform that can be access-controlled using a whitelist-source-range source annotation, by updating the related ingress template:
| Service | Recommendation | Ingress template |
|---|---|---|
| CDS (Common Data Service) | Admin access only | AIO/ingress/templates/cds-ingress.yaml |
| NiFi Registry | Admin access only | AIO/mlwb/nifi/kubernetes/ingress-registry.yaml |
| NiFi User | User access (required) | AIO/mlwb/nifi/templates/ingress.yaml |
| JupyterHub (Hub and User) | User access (required) | See note below |
| Kubernetes client | User access (required) | AIO/ingress/templates/k8s-client-ingress.yaml |
| Onboarding | User access (required) | AIO/ingress/templates/onboarding-ingress.yaml |
| Portal | User access (required) | AIO/ingress/templates/portal-ingress.yaml |
| MLWB Dashboard | User access (required) | AIO/mlwb/kubernetes/mlwb-dashboard-webcomponent-ingress.yaml |
| MLWB Home | User access (required) | AIO/mlwb/kubernetes/mlwb-home-webcomponent-ingress.yaml |
| MLWB Notebook | User access (required) | AIO/mlwb/kubernetes/mlwb-notebook-webcomponent-ingress.yaml |
| MLWB Notebook Catalog | User access (required) | AIO/mlwb/kubernetes/mlwb-notebook-catalog-webcomponent-ingress.yaml |
| MLWB Pipeline | User access (required) | AIO/mlwb/kubernetes/mlwb-pipeline-webcomponent-ingress.yaml |
| MLWB Pipeline Catalog | User access (required) | AIO/mlwb/kubernetes/mlwb-pipeline-catalog-webcomponent-ingress.yaml |
| MLWB Project | User access (required) | AIO/mlwb/kubernetes/mlwb-project-webcomponent-ingress.yaml |
| MLWB Project Catalog | User access (required) | AIO/mlwb/kubernetes/mlwb-project-catalog-webcomponent-ingress.yaml |
Notes on the table above:
- JupyterHub ingress rules are currently created by the deployment script in charts/jupyterhub/setup_jupyterhub.sh.
For other components, k8s nodeports are currently used for primary access or supplementatl access. Note that if possible, these services will be migrated to access via the ingress controller, early in the next release. However, in many cases these services may be provided as shared application services, and deployed outside the Acumos platform. The AIO toolset supports that as an option, which eliminates any concern about exposing these services as part of an Acumos platform:
| Service | NodePort (default) | Rational for NodePort Use | Security Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| CDS (Common Data Service) | 30800 | Alternative swagger UI (see note) | Apply firewall rule if needed |
| Docker Proxy | 30883 | Ingress rule is WIP (see note) | Leave open (required) |
| Federation (peer access) | 30984 | Ingress rule is WIP (see note) | Leave open (required) |
| Federation (local access) | 30985 | Ingress rule is WIP (see note) | Leave open (required) |
| Nexus (Maven) | 30881 | Admin access to Nexus UI (see note) | Apply firewall rule if needed, or use external service |
| Nexus (Docker) | 30882 | Admin access to Nexus Docker Registry (see note) | Apply firewall rule if needed, or use external service |
| JupyterHub | (dynamic ports) | Access to the Jupyter proxy (see note) | Apply firewall rule if needed |
| Security Verification (SV) Scanning Service | 30982 | Admin access to the SV service (see note) | Apply firewall rule if needed |
Notes on the table above:
- The CDS NodePort addresses current issues (under investigation) with access to the CDS swagger UI via HTTPS thru the ingress controller
- The Docker Proxy NodePort is currently required because an ingress rule for it has not been implemented/tested. An update will be published as soon as this has been done.
- Ingress support fort Federation NodePort is a WIP, like Docker Proxy. Use of a context path is hypothetically possible since peer configuration allows the use of a context path when defining the peer API endpoint; this just needs to be implemented/tested, and documented. An update will be published as soon as this has been done.
- Configuraton of JupyterHub to avoid NodePort use is a WIP.
- Access to the Security Verification Scan API is provided so that Admins can invoke scans manually or through external systems, and also for the future support of external scan result notifications.
7. Known Issues¶
Following are some things to watch out for in the process of deploying the Acumos platform with the AIO toolset. Solutions to improve the reliability of platform deployment are being implemented with each release, but this is a work-in-progress, and given that the Acumos platform deployment depends upon a number of upstream projects/components, issues such as the below may be encountered. This list will be updated as needed after the final Boreas release user guide is published, and will be available on the Acumos wiki at Hints and Known Issues
8. MariaDB Mirror Reliability¶
Periodically, the list of active mirrors for the MariaDB project may change. This can break Acumos installation at the point of setting up the MariaDB client, which is the only MariaDB component that needs to be installed on the platform host. The client enables the AIO tools to setup/upgrade the Acumos database as needed. If you encounter an AIO install failure of the type below, you will need to update the MariaDB mirror found in charts/mariadb/setup_mariadb_env.sh:
...
Reading package lists...
W: The repository 'http://ftp.utexas.edu/mariadb/repo/10.2/ubuntu xenial Release' does not have a Release file.
E: Failed to fetch http://ftp.utexas.edu/mariadb/repo/10.2/ubuntu/dists/xenial/main/binary-i386/Packages 403 Forbidden
E: Some index files failed to download. They have been ignored, or old ones used instead.
++ fail
++ set +x
fail:42 (Wed Jul 17 17:06:41 UTC 2019) unknown failure at setup_mariadb_client 70
If you see such a failure, select and configure a new MariaDB mirror from the MariaDB mirror list, as needed using a site such as the status of MariaDB mirrors to know which mirrors are active. Update the following line in charts/mariadb/setup_mariadb_env.sh and restart the deployment, selecting a new mirror host to replace ‘sfo1.mirrors.digitalocean.com’.
export MARIADB_MIRROR="${MARIADB_MIRROR:-sfo1.mirrors.digitalocean.com}"
You may also need to manually remove old/inactive MariaDB mirrors from /etc/apt/sources.list, if you get later errors from using ‘apt-get update’, via these commands:
sudo sed -i -- '/mariadb/d' /etc/apt/sources.list
sudo apt-get update